Classifying Living Things
Living vs. Nonliving
- Living things can Move, Reproduce, Sense, Grow, Respire, Excrete, Nourish.
- Also made of cells
- Living things are found either unicellular or multicellular
- Binomial Nomenclature (The Naming System)
-
- All living organisms can be grouped into Three domains: Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, and Eukarya and Six kingdoms: Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Animalia, Plantae, Fungi and Protista
- The classification hierarchy consists of:
Domain, Kingdom, Phyla, Classes, Orders, Families, Genera, and Species.
Dumb –> King –> Philip –> Came –> Over –> For –> Good –> Soup

-
- Any organism’s scientific name is written as: Genus species.
- E.g. Lion: Panthera leo or Panthera leo
- Any organism’s scientific name is written as: Genus species.
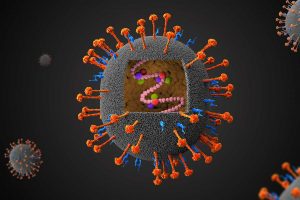
- Virus, Viroid and Prion
-
- These are only living when in a host cell.
- Viruses: have only genetic material surrounded by a protein that cause infections.
- These are only living when in a host cell.
-
-
- Viroid: is the RNA segments that cause infections.
- Prion: is the protein segments that cause infections.
-
THE THREE DOMAINS – SIX KINGDOMS SYSTEM
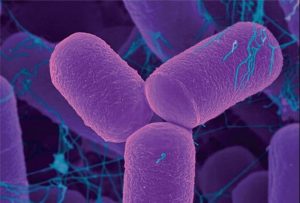
- Domain: Eubacteria
- Kingdom: Eubacteria.
- Prokaryotes: No nucleus; only a single chromosome.
- No membrane bound organelles.
- Unicellular.
- Cell wall made of peptidoglycan.
- Kingdom: Eubacteria.
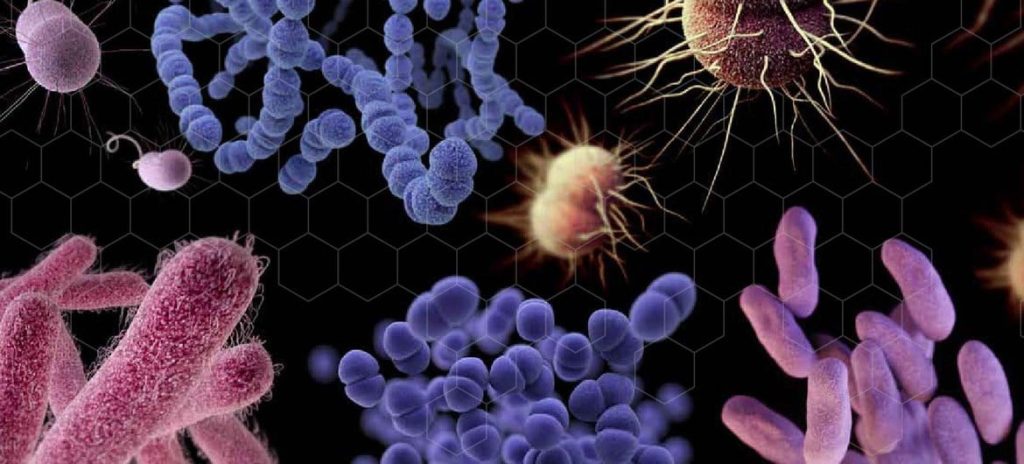
- Domain: Archaebacteria.
- Kingdom: Archaebacteria.
- Prokaryotes: No nucleus; only a single chromosome.
- No membrane bound organelles.
- Unicellular.
- Extremophiles: thrive in extreme conditions (E.g. Thermophiles).
- High similarities to eukaryotes.
- Kingdom: Archaebacteria.
- Domain: Eukarya.
- Kingdom: Fungi.
- Eukaryotes: contain at least one nucleus.
- Contain membrane bound organelles.
- Heterotrophic (Saprophytic: feed by external digestion).
- Unicellular (E.g. Yeast) and multicellular (E.g. Bread molds).
- Cell wall made of chitin.
- Live in moist, warm, full of nutrients and no light environment.
- Kingdom: Fungi.

-
- Kingdom: Protista.
- Eukaryotes: contain nucleus.
- Contain membrane bound organelles.
- Unicellular or multicellular.
- Contains three groups: Plant like Protista, Animal like Protista, and Fungus like Protista.
- Protophyta:
- Sometimes no cell wall.
- Sometimes heterotrophic.
- E.g.: Euglena, Diatoms, and Algae.
- Protophyta:
- Kingdom: Protista.
-
-
-
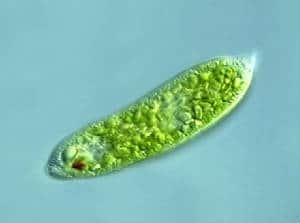
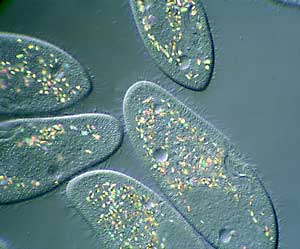
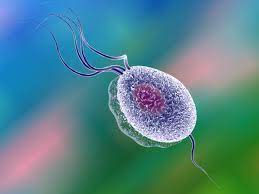
- Protozoa:
- No cell wall.
- All unicellular.
- E.g.: Giardia, Paramecium, Plasmodium, and Amoeba.
- Protozoa:
-
-
-
-
-
- Fungus like Protista:
- Cellulose cell wall.
- E.g.: Water molds and Slime molds.
- Fungus like Protista:
-
-

-
- Kingdom: Animals.
- Eukaryotes: contain nucleus.
- Contain membrane bound organelles.
- Heterotrophic.
- Multicellular.
- No cell wall.
- Kingdom: Animals.

-
- Kingdom: Plants.
- Eukaryotes: contain nucleus.
- Contain membrane bound organelles.
- Autotrophic: make their own food by photosynthesis because they contain chlorophyll.
- Multicellular.
- Cell wall made of cellulose.
- Kingdom: Plants.

DICHOTOMOUS KEY
- A method used to identify organisms by answering a series of questions.
- TYPE ONE: Identifying one organism.

-
- TYPE TWO: Identifying a group of organisms.